Snippet
def f(x: str) -> int:
return len(x) + 1
def g(x: int, y: str) -> int:
while x > len(y):
x -= 1
return x
def main() -> None:
(g(f("python"), "java"))
main()
Solution
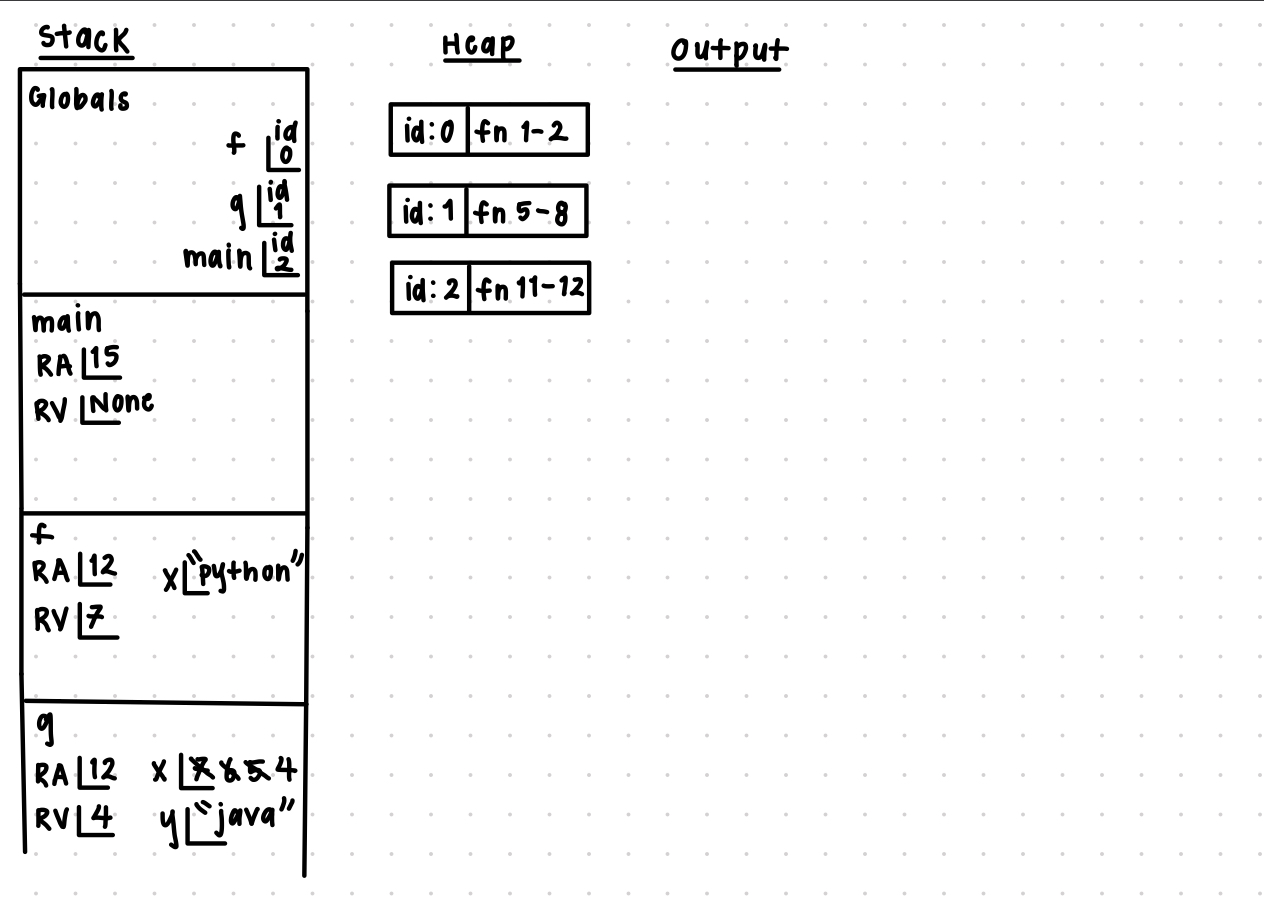
Image Description
The Memory Diagram includes three columns titled Stack, Heap, and Output.
The Stack includes 4 frames in the following order from top to bottom including Globals, main, f, and g.
The Globals frame has 3 variables including f, g, and main.
- f has id 0, it is a function on the Heap (lines 1-2).
- g has id 1, it is a function on the Heap (lines 5-8).
- main has id 2, it is a function on the Heap (lines 11-12).
The main frame has 2 items including the RA and RV.
- The RA is defined at line 15.
- The RV is None.
The f frame has 3 items including the RA and RV and a variable named x.
- The RA is defined at line 12.
- The RV is 7.
- x is “python”
The g frame has 4 items including the RA and RV and two variables named x and y.
The RA is defined at line 12.
The RV is 4
x is 4
Previous values of x include 7, 6, and 5 which are now crossed out * y is “java” The Heap includes 3 function objects. Output is empty.